The Neurobiological Basis for Schizophrenia Discussion
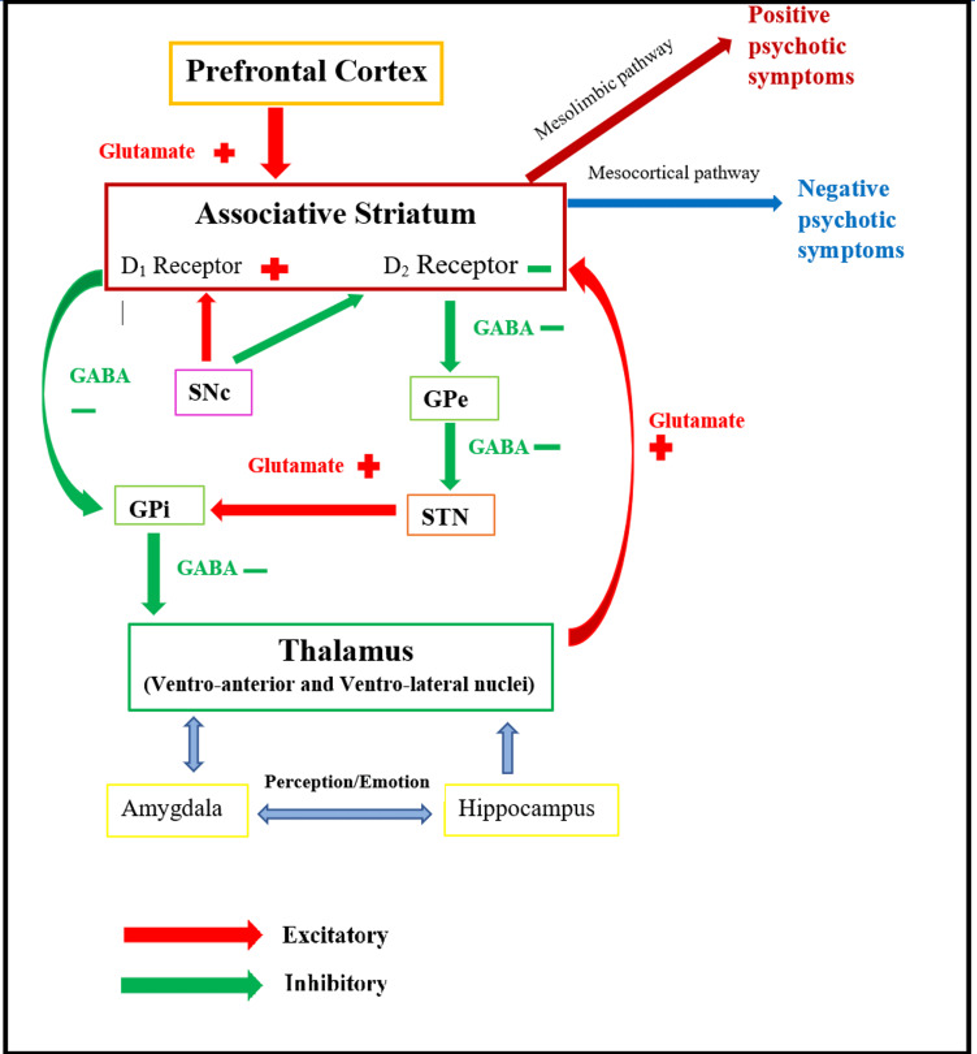
Schizophrenia is a disease that results in psychosis and decreased functioning. It is an exhausting disease that presents negative and positive symptoms affecting emotions and cognition. The different onset and features of schizophrenia are relates with the interaction of various neurotransmitters. However, subcortical dopamine dysfunction is the main cause in schizophrenia symptoms. The positive symptoms of schizophrenia show the availability of exaggerated perceptions, ideas, and actions, while negative symptoms show inadequacy in the normal mental functioning. According to Luvsannyam et al. (2022)The Neurobiological Basis for Schizophrenia Discussion, the presence of different schizophrenia symptoms shows the interaction of the neurotransmitters, particularly dopamine, in the mesostriatal, temporal, and brain regions. The positive symptoms are associated with abnormal dopamine levels in mesolimbic circuits, particularly the nucleus accumbens. The nucleus accumbens is an element of the brain’s reward pathway and may be the source of common comorbid substance use concerns. On the other side, the PFC, particularly the ventromedial and mesocortical PFC, is linked with the negative and affective impacts of schizophrenia. The cognitive symptoms are linked to the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, while the orbitofrontal cortex and the amygdala are connected with the impulsive and aggressive symptoms of schizophrenia.
ORDER YOUR PAPER HERE
Classes of Medication for Schizophrenia Treatment
Schizophrenia is treated using antipsychotic medications. They are grouped into different classes; conventional antipsychotics and atypical antipsychotics.
Atypical Antipsychotics
Atypical antipsychotics are serotonin-dopamine antagonists. According to Chokhawala and Stevens (2022), they function by blocking D2 dopamine receptors as well as serotonin receptor antagonist action, with the 5HT2A serotonin receptors being the one commonly used. They have different degrees of affinity for 5HT2A and D2 receptors. For example, the “dones” such as paliperidone, risperidone, ziprasidone, iloperidone, and lurasidone bind more potently to 5HT2A receptors compared to the D2 receptors or exhibit similar potency for the two receptors. The ‘pines” such as clozapine, asenapine, olanzapine, and quetiapine also bind more potently to the 5HT2A receptors compared to the D2 receptors. On the other side, cariprazine and aripiprazole bind more potently to the D2 receptors than 5HT2A, while brexpiprazole has similar binding potency to both receptors The Neurobiological Basis for Schizophrenia Discussion.
They are effective in treating the positive and negative features of schizophrenia. They are, however, associated with various side effects, including causing the metabolic syndrome and serious weight gain. It is thus important to analyze and monitor a person’s history and family history of diabetes mellitus, blood pressure, height, weight, dyslipidemia, fasting plasma glucose, and waist circumference of all patients (Chokhawala & Stevens, 2022). Specifically, risperidone is associated with sedation, anxiety, and dizziness, olanzapine causes increased appetite, tiredness, and weight gain, while aripiprazole causes headaches, agitation, and restlessness. Asenapine causes increased concentrations of serum prolactin and weight gain, and clozapine causes tachycardia, hypersalivation, and hypotension. It is also associated with agranulocytosis and leukopenia, thus requiring close keep track of leukocytes and neutrophil count. According to the FDA requirements, the absolute neutrophil count should be monitored every week for six months, and if normal, it can be checked in two weeks (Chokhawala and Stevens, 2022). This ensures the effectiveness of the medication and the regulation of any side effects.
Conventional Antipsychotics
Conventional antipsychotics work through antagonism of the D2 receptors. They work almost exclusively on the dopamine system, with their activity being best when approximately 72% of the dopamine receptors in the brain is blocked (Chokhawala & Stevens, 2022)The Neurobiological Basis for Schizophrenia Discussion. They function by attaching to D2 receptors and then quickly detaching to allow for normal transmission of dopamine. This consequently maintains normal prolactin levels, spares cognition, and obviates EPS. Thus, while promoting positive effects, it causes various undesirable effects, including EPS, TD, and hyperprolactinemia. The antagonism action on D2 worsens the negative effects of schizophrenia. In the nucleus accumbens, the reward center blocks reward mechanisms causing the patient to be numb and anhedonic. They thus lack interest and motivation and become socially withdrawn.
Substantial blockage of D2 in the nigrostriatal DA pathway causes movement disorders and sometimes Tardive Dyskisenia. Additionally, conventional antipsychotics cause blockage of dopamine D2 receptors in the tuberoinfundibular DA pathway, which results in hyperprolactinemia and increased plasma prolactin concentrations. This can cause fertility problems in younger women, bone demineralization in post-menopausal women, and impotence in men (Chokhawala & Stevens, 2022). On top of this, blockage of muscarinic receptors results in side effects such as dry mouth, constipation, and blurred vision. Histamine antagonism also causes drowsiness. According to Chokhawala and Stevens (2022), conventional antipsychotics may result in neuroleptic malignancy, which is characterized by extremely high temperatures, confusion, extreme muscular rigidity, agitation, acute renal failure, increased liver enzymes, increased white blood cell count, myoglobinuria and increased creatinine phosphokinase concentrations. In such cases, the antipsychotic should be immediately discontinued, followed by cooling and adequate hydration, and close monitoring.
Recommended Medication and Education
For this case, atypical antipsychotics would be recommended, particularly risperidone. According to Chokhawala and Stevens (2022), compared to conventional antipsychotics, atypical antipsychotics have low risks of extrapyramidal side effects. Additionally, compared to conventional antipsychotics, atypical antipsychotics are characterized by a clinical profile of similar positive symptoms but low extrapyramidal symptoms and less hyperprolactinemia. By blocking 5HT2A receptors on glutamatergic pyramid neurons, they inhibit glutamate release resulting in increased dopamine release in the striatum and reduced prolactin release. This consequently inhibits extrapyramidal symptoms. Also, in the tuberoinfundibular dopamine and the nigrostriatal pathway, there is enough dopamine released by atypical psychotics to reverse, in part, the undesirable effects of hyperprolactinemia and EPS. While conventional antipsychotics treat the positive effects of schizophrenia, atypical antipsychotics are effective in treating both positive characteristics of schizophrenia, such as hallucinations and delusions, and negative features, including ambivalence and withdrawal, and reduce relapse rates (Chokhawala & Stevens, 2022)The Neurobiological Basis for Schizophrenia Discussion. With Shawn exhibiting both positive and negative features of schizophrenia, atypical antipsychotics are more effective for his treatment.
Risperidone is recommended for treatment for various reasons. It reduces/eliminates both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Additionally, they have mild side effects and can easily help one reach their treatment goals. According to Correll et al. (2020), risperidone effectively improves patients’ positive and negative characteristics, with studies demonstrating its efficacy, tolerability, and safety.
It is, however, important to note that cardiometabolic effects are a concern with all antipsychotic drugs. However, the risk is not high with atypical antipsychotics and can be experienced at varying degrees. Therefore, with antipsychotics, the patient needs to have various lifestyle considerations and adjustments. They should observe their diet and exercise as it relates to the cardiometabolic effects. Shawn should thus exercise regularly, eat a healthy diet and avoid smoking.
ORDER HERE
Evaluation of Efficacy
With the goal being remission or reduction of the psychotic symptoms, the efficacy of the drugs can be determined by evaluating the psychotic symptoms exhibited by the patient. According to Haddad and Correll (2018), antipsychotic efficacy in schizophrenia is determined by the targeted symptoms and how effective the drug was. It depends on the effectiveness in treating the symptoms or reducing the overall symptoms and how effective it was in producing the desired results. Shawn presented isolation, lack of interest in conversation or peer activities, and lacking motivation, and engaging in a conversation with someone who was not there. The efficacy of the medication used can be evaluated by these symptoms by comparing before and after administration of the medication. If the drugs effectively intervened and produced the desired results, the drugs has high efficacy. On the other side, if the medication did not effectively produce the desired results, the medication has low efficacy. The Neurobiological Basis for Schizophrenia Discussion